SIP (CTA and UTP Plan) and Identifiers
Terminologies:
- CTA: Consolidated Tape Association
- UTP: Unlisted Trading Privileges
- CTS: Consolidated Tape System
- CQS: Consolidated Quote System
- UTDF: UTP Trade Data Feed
- UQDF: UTP Quote Data Feed
- Tape A: NYSE listed securities
- Tape B: NYSE Arca and Amex listed securities
- Tape C: Nasdaq listed securities
- FINRA: Financial industry regulatory authority
tl;dr CTA distributes trade(CTS) and quote(CQS) messages for tape A (i.e. NYSE listed securities) and tape B (i.e. NYSE Arca and Amex). UTP distributes trade(UTDF) and quote(UQDF) messages for tape C (i.e. Nasdaq listed securities)
When I first entered finance, one of the few jargons that confused me was SIP, then came CTA and UTP. These acronyms are thrown around by those who work in finance all the time and while I kind of knew what they were, I never dug deep into them until recently. Here is all you need to know about them:
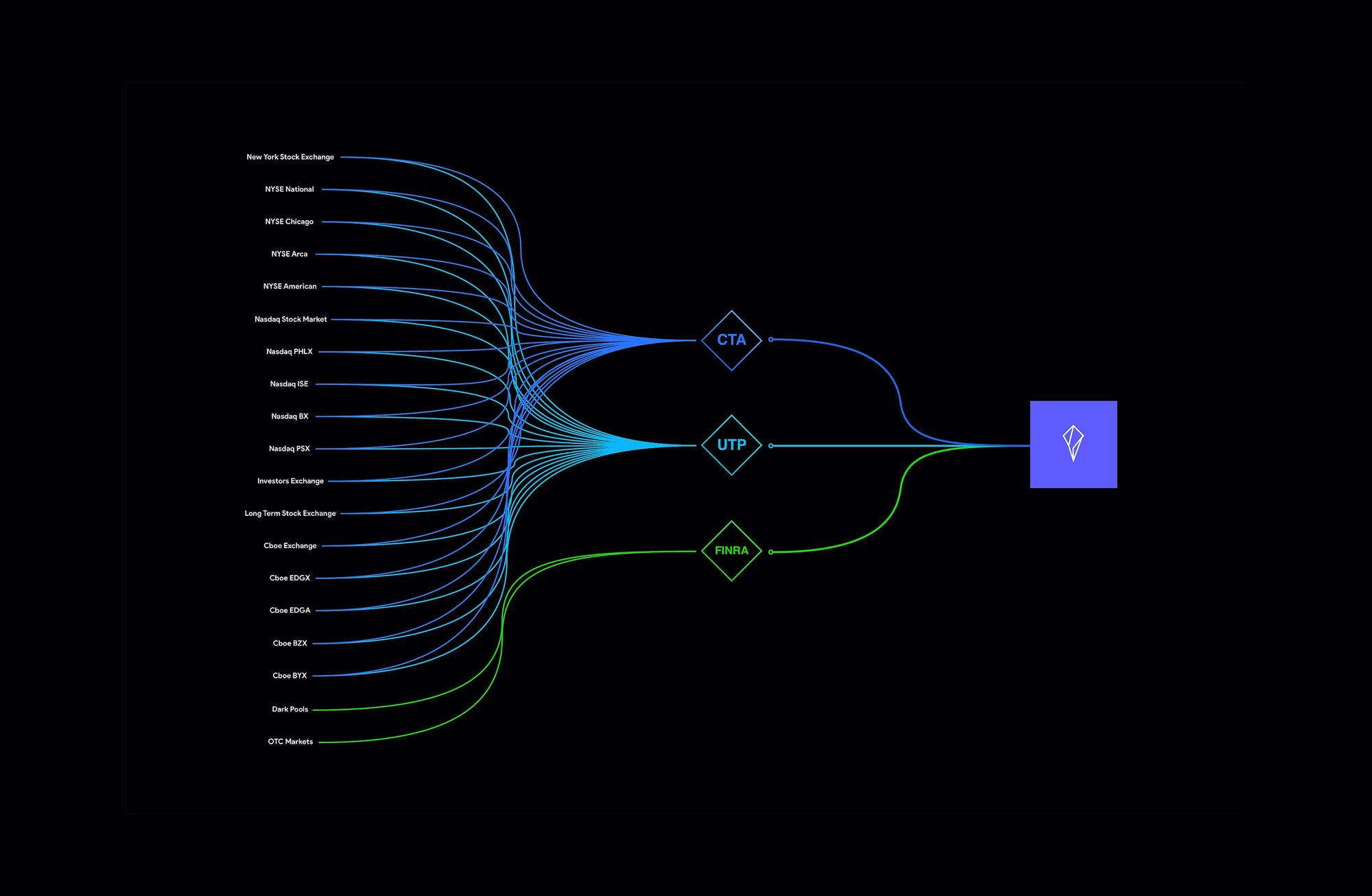
CTA (Consolidated Tape Association)
When someone says CTA, they are referring to the association that oversees the consolidation and distribution of NYSE listed securities (Tape A) and NYSE Arca & Amex listed securities (Tape B).
UTP (Unlisted Trading Privileges) Plan
Similary, when someone says UTP, they are referring to the association that oversees the consolidation and distribution of Nasdaq listed securities (Tape C).
CTS (Consolidated Tape System) and CQS (Consolidated Quote System)
CTS and CQS are data feed provided by the CTA. CTS consolidates and distributes Tape A and Tape B trades. CQS consolidates and distributes Tape A and Tape B quotes.
UTDF (UTP trade data feed) and UQDF(UTP quote data feed)
UTDF and UQDF are data feed provided by the UTP Plan. UTDF consolidates and distributes Tape C trades. UQDF consolidates and distributes Tape C quotes.
SIP (securities information processor)
SIP refers to any system that consolidates and distributes market data to public. In the U.S., there are two sips: CTA and UTP Plan.
In addition to trades and quotes, both SIPs provide additional data which include
- National best bid and offer (NBBO)
- Limit up and down (LULD) price bands
- Trading halts
- IPOs
- Financial status
Here’s a nice image from Peter Stacho:
Terminologies:
- ISIN: international securities identification number
- CUSIP: Committee on Uniform Security Identification Procedures
- SEDOL: Stock Exchange Daily Official List
- RIC: Reuters Instrument Code
There are many ways to uniquely identify a security but most will use ISIN (since it’s an expansion of SEDOL and CUSIP, which we will discuss more in this post). Here we list a few well known identifiers:
Ticker
The most naive way to identify a security is by the ticker symbol – this is used to identify publicly traded shares of a particular stock on a given exchange.
Most won’t use the ticker symbol since it doesn’t contain any information on where it is traded and what type of security it is. For instance, AAPL doesn’t tell us whether we are referring to AAPL that is being traded in the U.S. or U.K. Additionally, we don’t know if we are referring to AAPL stock or AAPL bond.
RIC
Reuters instrument code used in Refinitiv services to identify companies. Only Refinitiv products use it and no one else, but since Refinitiv is such a huge data service provider, you’ll probably uses it at some point if you’re in finance.
SEDOL
SEDOL stands for Stock Exchange Daily Official List – they are 7 characters in length, a 6 place alphanumeric code and a trailing check digit. These numbers are used to identify securities by the London Stock Exchange. SEDOLs serve as the National Securities Identifying Number for all securities in the U.K. therefore it is part of security’s ISIN as well.
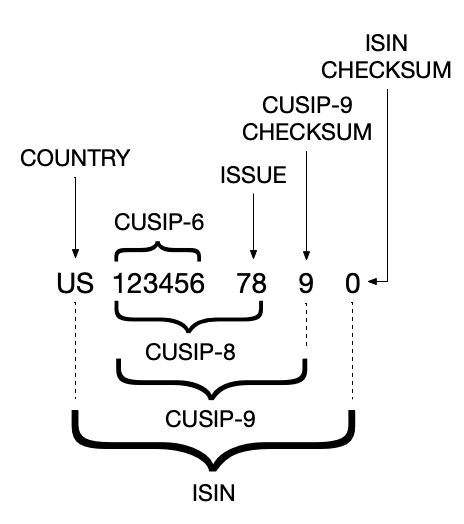
CUSIP
Similarly, CUSIP stands for Committee on Uniform Security Identification Procedures and contains 6, 8 or 9 digit alphanumeric code which identifies a North American equity. They are created by the American Banking Association and are operated by S&P Capital IQ. Since CUSIPs are unique identifiers for U.S. securities, they are used as part of security’s ISIN as well.
ISIN
ISIN stands for international securities identification number and it is a 12-digit alphanumeric code that uniquely identifies a specific security globally. There are three parts to ISIN: (i) country code, (ii) numbers, and (iii) checksum. For securities in U.K., the number would be SEDOL while for U.S. securities, it is CUSIP.
Here’s a simple diagram on how ISIN is generated from CUSIP:
Most financial data providers, e.g. Thomson Reuters, Bloomberg, BvD, usually include an ISIN number.

Leave a comment